Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. The liver is responsible for processing and metabolizing fats from the bloodstream, but when there is an excessive build-up of fat in the liver cells, it can lead to fatty liver disease. There are two main types of fatty liver:
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD is the most common form of fatty liver and occurs in individuals who do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol. It is often associated with conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can range from simple fatty liver, which typically does not cause serious health issues, to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is a more severe form associated with inflammation and liver damage. NASH can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer if not managed.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. When alcohol is consumed, the liver prioritizes its metabolism, which can lead to the accumulation of fat in liver cells. Over time, excessive alcohol use can result in alcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and other serious liver complications.
How common is Fatty Liver in India?
A recent AIIMS study, which analysed published reports on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in India, states that over one-third (38 per cent) of Indians have fatty liver or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
The phenomenon is not restricted to adults, but affects nearly 35 per cent of the children as well, says the study published in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hepatology in June 2022.
What are the causes of Fatty Liver?
Here are the primary causes of fatty liver in bullet points:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
-
Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is a major risk factor.
-
Insulin Resistance: Reduced sensitivity to insulin, often associated with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
-
High Sugar and High-Fat Diet: Consuming excessive amounts of sugar and unhealthy fats can contribute.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can increase the risk of NAFLD.
-
Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like dyslipidemia (abnormal blood lipid levels) and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can be associated with NAFLD.
-
Rapid Weight Loss: Sudden and significant weight loss, such as with crash diets or bariatric surgery, can lead to fatty liver.
-
Medications: Certain medications, including corticosteroids and some antiviral drugs, can contribute to NAFLD.
- Genetic Factors: Family history and genetics may play a role in susceptibility.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
-
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: The primary cause of AFLD is the chronic and excessive consumption of alcohol.
- Amount and Duration: The risk of AFLD increases with the quantity and duration of alcohol intake.
What are the symptoms of Fatty Liver disease?
Fatty liver disease, both non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD), can be asymptomatic in its early stages, and many people may not experience noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they are often vague and nonspecific.
Common symptoms of fatty liver disease may include:
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or lacking energy is a common symptom.
- Right Upper Abdominal Discomfort: Some individuals with fatty liver may experience a dull or aching pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: In some cases, there may be unexplained weight loss, especially with more advanced liver disease.
- Weakness: A general feeling of weakness or malaise.
- Loss of Appetite: A decreased interest in eating and a loss of appetite can occur.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may occur, particularly in more severe cases.
It's important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to fatty liver disease and can be caused by various other medical conditions. Additionally, many people with fatty liver disease may not experience any symptoms at all. Therefore, diagnosing fatty liver often requires medical evaluation, including blood tests and imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI.
Fatty liver disease can progress to more severe stages, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and liver failure, without causing significant symptoms in its early stages. Regular check-ups and liver function tests are essential for early detection and intervention.
Fatty Liver treatment in Ayurveda:
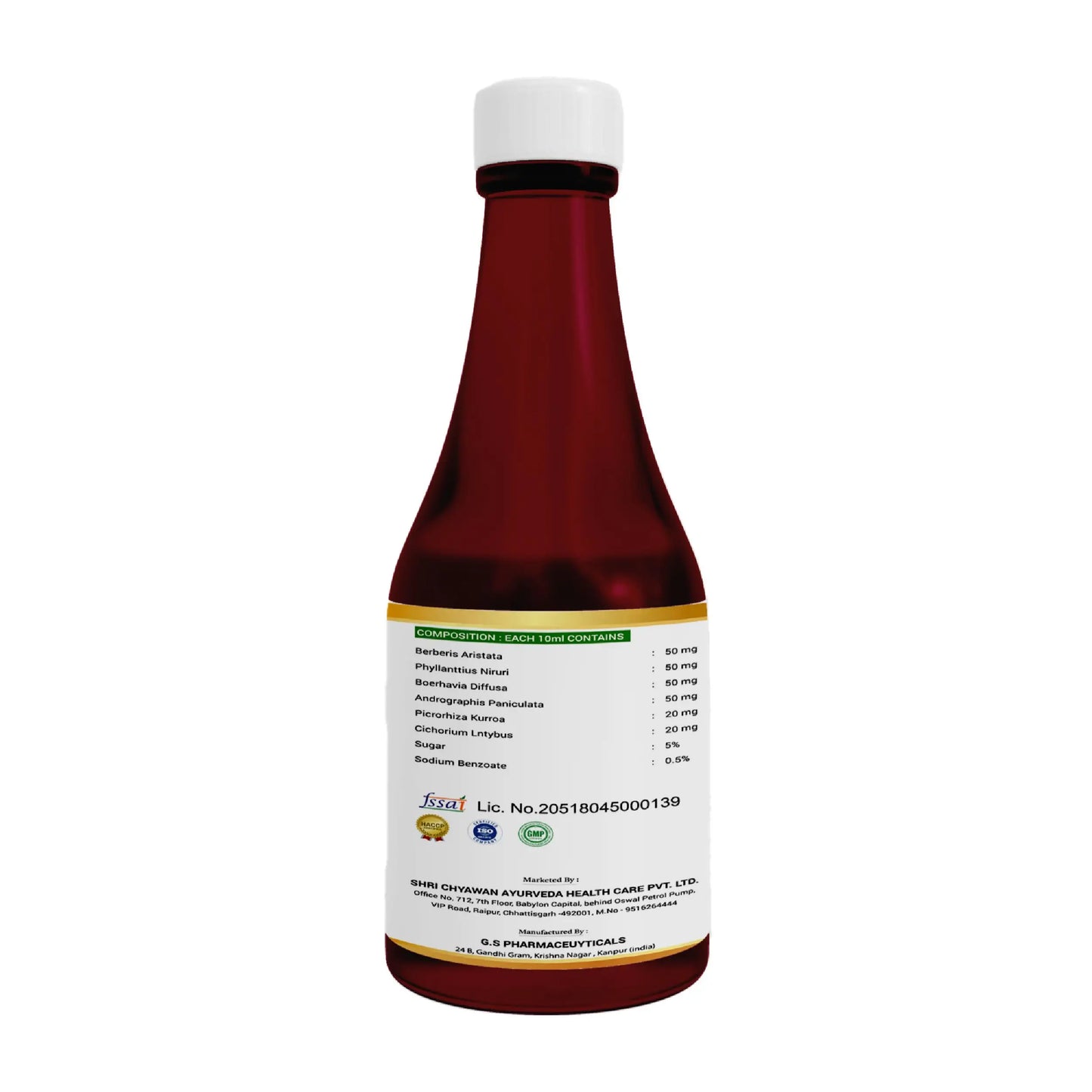
Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's has formulated an ayurvedic syrup for Liver, Liver Care Syrup with the aim to cleanse your liver and support digestion process. It also helps to strengthen the overall functioning of the liver. It is the best ayurvedic syrup for fatty liver.
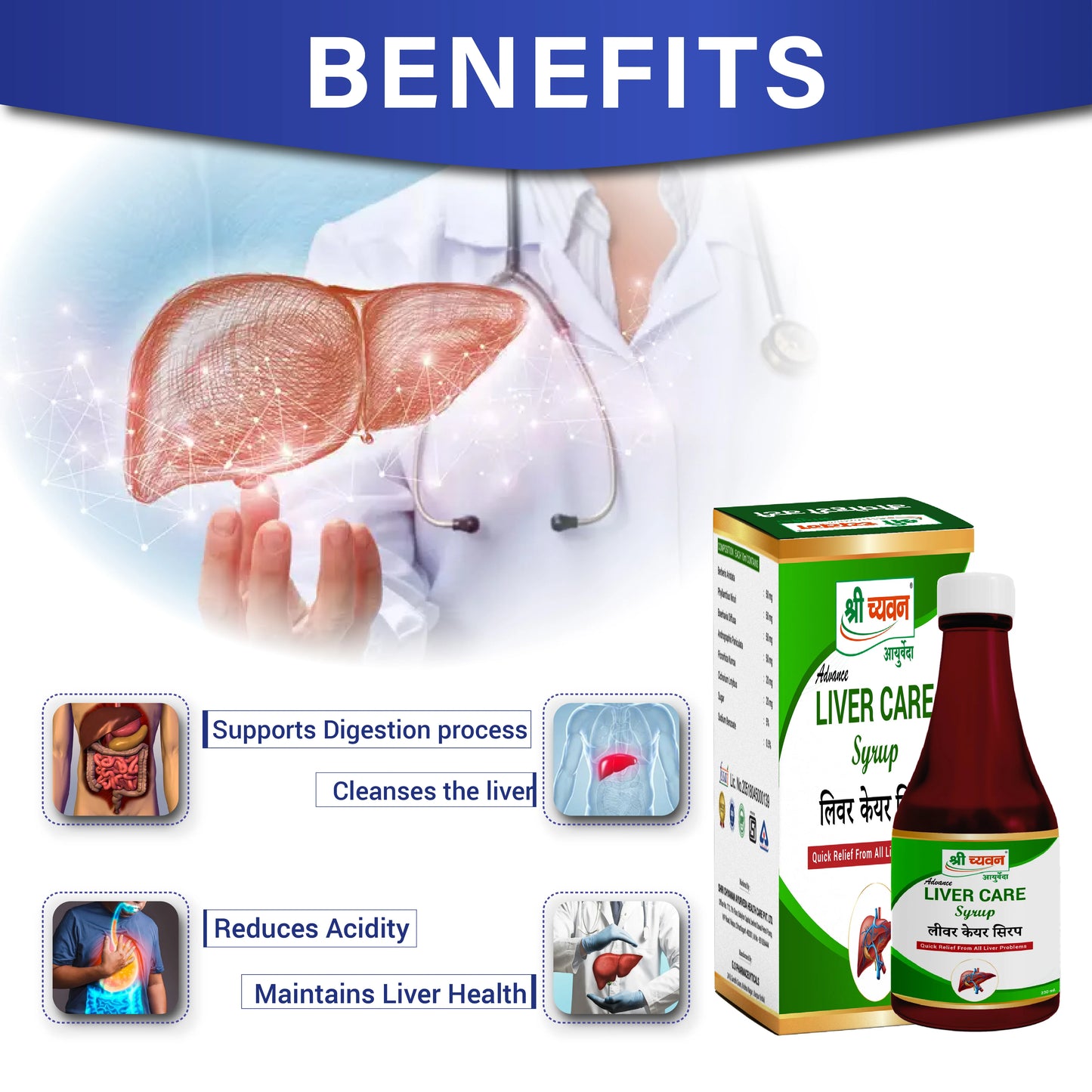
Liver Care Syrup Benefits:
-
Reduces Acidity: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Liver Care Syrup, best liver tonic in ayurveda helps in reducing acidity and also reduces acid reflex issues as well.
-
Detoxifier: Liver Care Syrup, an ayurvedic syrup for liver acts as a detoxifying agent and flushes out toxins from your body.
-
Aids in Digestion: It also helps in digestion of food and boosts metabolism and solves constipation problem as well.
- Maintains Liver Health: Regular intake of ayurvedic liver tonic Liver Care Plus Syrup helps to maintain Gut and Liver health.
- Protection from Liver Damage: Certain ingredients in liver care syrups, such as milk thistle (silymarin) and turmeric (curcumin), are believed to have hepatoprotective properties, meaning they may protect the liver from damage caused by toxins, alcohol, medications, or infections.
- Liver Regeneration: Some ingredients may support liver cell regeneration and repair, which can be beneficial in cases of liver damage or disease.
- Balanced Cholesterol Levels: Liver care syrups may help maintain healthy cholesterol levels by supporting the liver's role in cholesterol metabolism.
- Gut Health: A healthy liver can indirectly benefit gut health by promoting proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Energy and Vitality: When the liver is functioning optimally, it can aid in the metabolism of nutrients and energy production, potentially leading to increased vitality and reduced fatigue.
- Natural Product: It is made from all herbal, ayurvedic ingredients and is natural and safe to use.
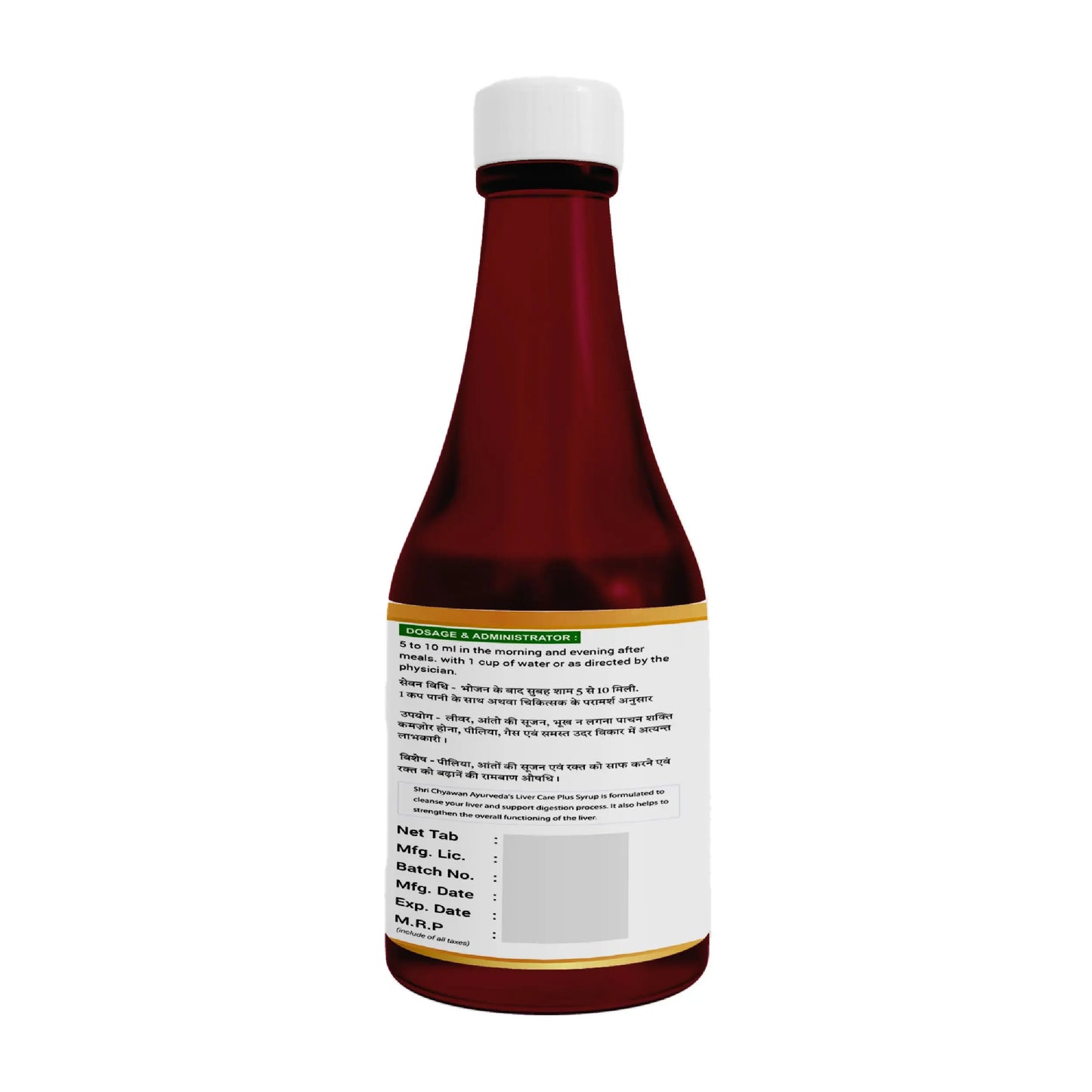
How to use: Consume 1-2 teaspoonful of Liver Care Syrup, thrice a day or as suggested by your physician.
In conclusion, liver care syrup an ayurvedic liver tonic, offer a range of potential benefits for liver health, including detoxification, liver function support, protection from damage, improved digestion and more. However, it's essential to use these supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional and as part of a comprehensive approach to liver health that includes a healthy lifestyle.