Introduction
Overview of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. They vary in size and can cause significant pain and discomfort as they pass through the urinary tract. Understanding the types and causes of kidney stones is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Importance of Dissolving Kidney Stones
Dissolving kidney stones can help alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and avoid invasive procedures. Effective dissolution methods reduce the risk of stones causing blockages or infections, improving overall kidney health and quality of life.
Understanding Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are small, hard mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys. They can vary in size and composition, and their presence can lead to significant discomfort and health complications. Here, we’ll delve into the different types of kidney stones and the causes and risk factors associated with their formation.
Types of Kidney Stones
- Composition: These are the most common type, consisting mainly of calcium combined with oxalate, a compound found in many foods.
- Appearance: Typically small and can vary in color from white to brownish-yellow.
- Formation: High levels of calcium or oxalate in the urine, often due to dietary habits or metabolic disorders.
- Composition: Composed of calcium and phosphate, these stones are less common than calcium oxalate stones.
- Appearance: Usually smooth and white or light-colored.
- Formation: Often associated with metabolic conditions such as renal tubular acidosis or specific types of kidney diseases.
- Composition: Formed from magnesium, ammonium, and phosphate, struvite stones are often associated with urinary tract infections.
- Appearance: Generally larger and can have a rough surface with a beige or yellow color.
- Formation: Develops in response to urinary tract infections that produce enzymes breaking down urea into ammonia, creating an environment conducive to stone formation.
- Composition: Made from uric acid, a waste product normally excreted by the kidneys.
- Appearance: Smooth and can be yellow to reddish-brown.
- Formation: Often associated with conditions that lead to high levels of uric acid in the urine, such as gout or a diet high in purines (found in red meat and certain fish).
Causes and Risk Factors
- Impact: Insufficient fluid intake leads to concentrated urine, which increases the likelihood of stone formation.
- Prevention: Drinking plenty of water to maintain proper hydration levels.
- Impact: High intake of calcium, oxalate, or sodium can contribute to stone formation. Conversely, a diet low in calcium can also increase risk, as calcium binds with oxalate in the intestines, reducing its absorption.
- Prevention: Balanced diet with moderate calcium and low oxalate and sodium intake.
- Impact: Family history of kidney stones can increase the likelihood of developing them.
- Prevention: Genetic factors are less modifiable, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage risk.
- Impact: Conditions such as gout, diabetes, or hyperparathyroidism can influence stone formation. Certain diseases affecting the kidneys or bladder can also increase risk.
- Prevention: Managing underlying medical conditions and regular medical check-ups can help mitigate risk.
- Impact: Sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and lack of physical activity can contribute to stone formation.
- Prevention: Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce risk.
- Impact: Some medications can affect the composition of urine, leading to stone formation.
- Prevention: Consultation with a healthcare provider for alternatives or adjustments in medication if necessary.
Understanding these types and risk factors is key to preventing kidney stones and managing them effectively if they occur. Regular medical check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are essential for reducing the likelihood of developing these potentially painful stones.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Common Symptoms Kidney stones can cause a range of symptoms, which may vary depending on the size and location of the stone. Common symptoms include:
- Severe Pain: Often described as sharp or cramping, typically in the lower back or side, and may radiate to the abdomen or groin.
- Hematuria: Blood in the urine, which may appear pink, red, or brown.
- Frequent Urination: Increased urge to urinate, sometimes with pain or burning sensation.
- Nausea and Vomiting: May occur due to the body's response to pain.
- Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine: Indicating possible infection or stone presence.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or burning sensation during urination.
When to Seek Medical Help It’s crucial to seek medical attention in the following situations:
- Severe Pain: Intense or worsening pain that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter pain relief.
- Blood in Urine: Significant or persistent blood in urine, especially if accompanied by pain.
- Infection Symptoms: Fever, chills, or symptoms of an infection such as cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
- Urinary Blockage: Difficulty urinating, or an inability to pass urine, which could indicate a blockage.
- Persistent Symptoms: Symptoms that do not improve or worsen over time.
Prompt medical evaluation can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and determine the appropriate treatment for kidney stones.
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the kidneys and urinary tract to identify stones.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to detect stones, particularly useful for pregnant women and children.
- X-rays: Traditional X-rays can reveal larger stones but may miss smaller ones.
Interpreting Test Results
Accurate diagnosis helps guide treatment options and management strategies for kidney stones.
Conventional Treatments
Medication Options
Surgical Procedures
Choosing the right treatment depends on the size, type, and location of the stones, as well as the patient's overall health.
Natural and Home Remedies
Dietary Changes
- Reduce Sodium: Lower sodium intake to decrease calcium in the urine, which can help prevent stones.
- Limit Oxalate-Rich Foods: Reduce consumption of foods high in oxalates, such as spinach, nuts, and chocolate, which can contribute to calcium oxalate stones.
- Increase Citrus Fruits: Consuming citrus fruits like lemons and oranges can increase citrate levels in urine, which helps prevent stone formation.
Hydration and Fluid Intake
- Drink Plenty of Water: Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily to dilute urine and help flush out stones.
- Avoid Excessive Caffeine and Alcohol: Limit intake of caffeinated and alcoholic beverages as they can contribute to dehydration.
Herbal Remedies and Supplements
- Dandelion Root: Known for its diuretic properties, it may help increase urine flow and support kidney health.
- Chanca Piedra: Often called the "stone breaker," this herb is traditionally used to help dissolve kidney stones.
- Nettle Leaf: May help support kidney function and reduce inflammation.
These natural and home remedies can complement conventional treatments and aid in the prevention and management of kidney stones. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting new remedies or supplements.
Ayurvedic Approaches
Ayurvedic Herbs and Formulations
Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
Ayurvedic approaches combine these herbs and lifestyle practices to support kidney health, prevent kidney stones, and promote overall well-being. Always consult with an Ayurvedic practitioner to tailor these recommendations to your individual health needs.
Preventing Kidney Stones
Long-Term Dietary Adjustments
Lifestyle Changes and Monitoring
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of kidney stones and promote long-term kidney health.
Shri Chyawan's Ayurvedic Solution
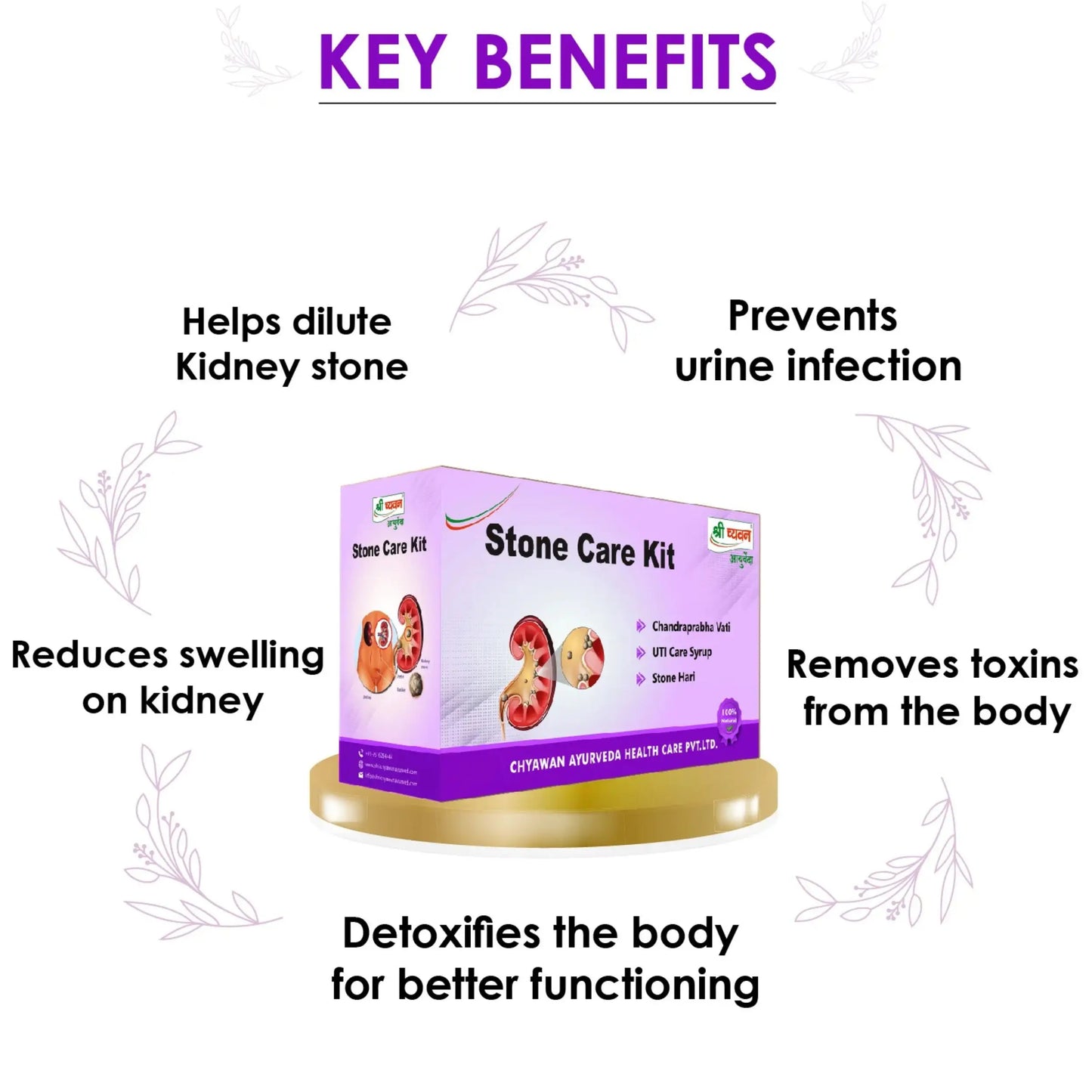
Stone Care Kit: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda has effectively formulated ayurvedic medicine for Kidney Stone - Stone Care Kit. Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and acid salts that stick together in concentrated urine. They can be painful when passing through the urinary tract, but usually don't cause permanent damage. This is the best product range available for your entire kidney stone ayurvedic treatment.
1. Chandrabha vati: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Chandraprabha vati helps to reduce the level of uric acid, which aids in controlling diabetes.
Ingredients: It consists of Amla, Sandalwood, Daruharidra, Devdaru, Camphor, Cinnamon, and Pipal.
How To Use: Consume 1 tablet at night before going to bed.
2. Stonehari Vati: It is a really effective ayurvedic medicine for Kidney Stone, Gallbladder Stone and other kidney related disease. It is the best kidney stone ayurvedic tablet.
Ingredients: This contains ingredients like Mulkshar, Hajratyahudbhasam, Punarnava, Gokhru, Varun Chal, Jamun Chal, Vajra Chal, Vajra parpati, Swet parpati, Pashanabhed.
How to use: One tablet thrice a day or as directed by the physician.
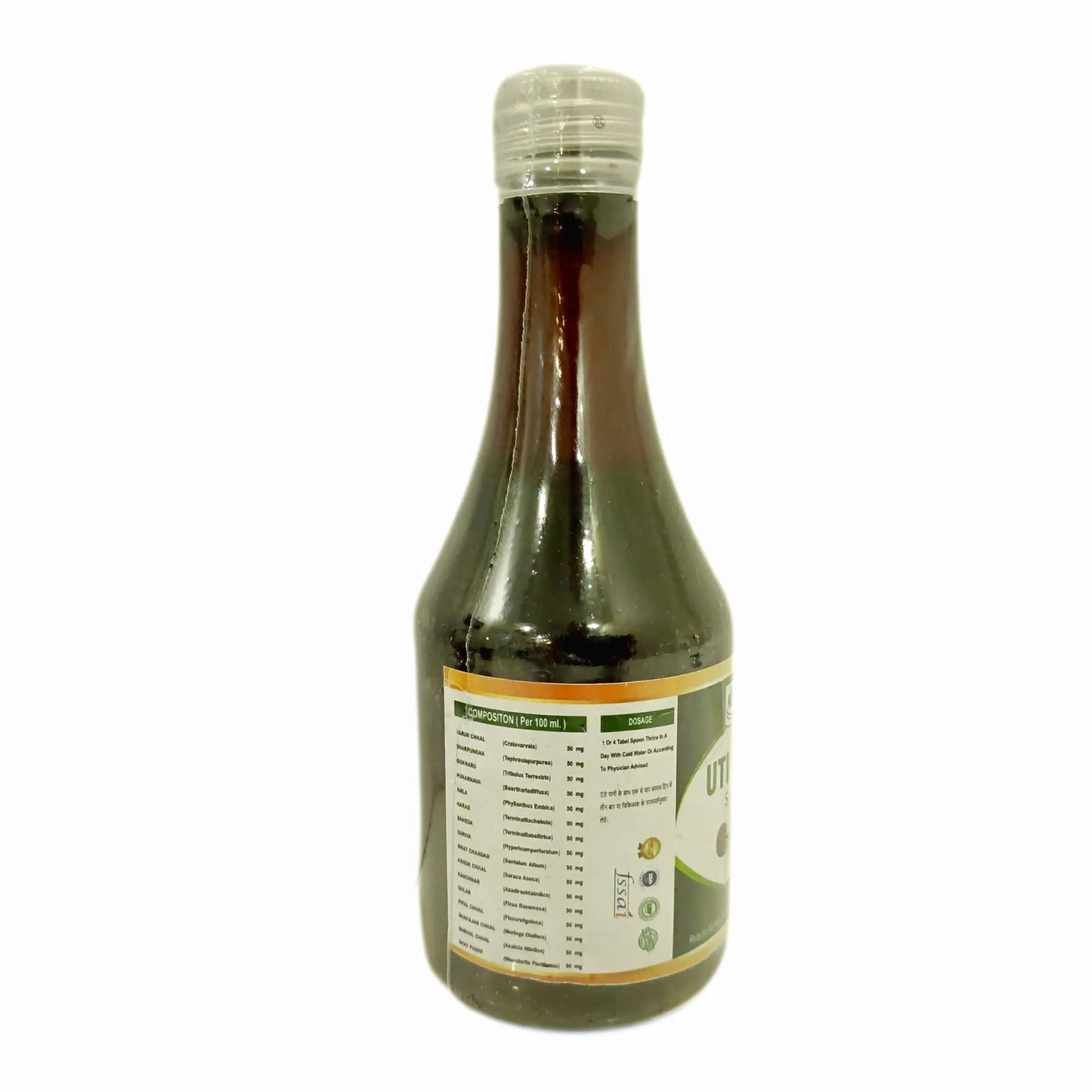
3. Uti Care Syrup: It is useful in Urine Infection and Urine blockages. It also acts as a detoxifier for your body and cleanses your system. It is the most recommended kidney stone ayurvedic syrup.
Ingredients: It consists of mainly Varun Chal, Sharpunkha, Gokharu, Punarnava, Amle, Harde, Baheda, Sariva, Swat Chandan, Ashok Bark, Kanchanar, Gullar Fruit, Pipar Bark, Drumstick Bark, Babbol Bark, Dhatkipuspa.
How to use: Consume1 teaspoon thrice a day with cold water or as directed by the physician.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Signs That Require Medical Attention
Preparing for a Medical Consultation
Consulting a healthcare professional with this preparation will help ensure a thorough evaluation and facilitate an effective treatment plan for managing and preventing kidney stones.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
- Understanding Kidney Stones: Kidney stones are solid mineral deposits that form in the kidneys, varying in type and size. They can cause significant pain and discomfort as they pass through the urinary tract.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves urinalysis, imaging studies (CT scan, ultrasound), and sometimes an intravenous pyelogram (IVP) or stone analysis to determine the type and location of stones.
- Conventional Treatments: Treatment options include medications for pain and stone dissolution, as well as surgical procedures like shock wave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy for more severe cases.
- Natural and Home Remedies: Dietary changes, increased hydration, and herbal remedies can support stone prevention and management. A balanced diet, ample fluid intake, and specific herbs like Chanca Piedra and Gokshura are commonly used.
- Ayurvedic Approaches: Ayurveda offers herbs such as Chanca Piedra and Punarnava, along with lifestyle and dietary recommendations tailored to balance the body's doshas and support kidney health.
- Prevention: Long-term prevention strategies include dietary adjustments, adequate hydration, regular exercise, and routine medical monitoring to reduce the risk of kidney stone formation.
Final Tips for Managing Kidney Stones
By integrating these practices into your lifestyle, you can effectively manage and reduce the risk of kidney stones, contributing to overall kidney health and well-being.
Free Consultation with our Expert Doctor- 📞📞 95162 64444