Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of fat (triglycerides) in liver cells (hepatocytes). While it's normal for the liver to contain some fat, excessive fat build-up can be harmful and interfere with the liver's normal functioning.
There are two main types of fatty liver:
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD is the most common form of fatty liver and is not related to excessive alcohol consumption. It typically occurs in individuals who have risk factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, or metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can range from simple fatty liver (steatosis) to a more severe form called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to liver inflammation and scarring (fibrosis).
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. The liver metabolizes alcohol, and when it's consumed in excess, it can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver. AFLD can progress to more severe liver conditions, such as alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis, if alcohol abuse continues.
Both NAFLD and AFLD can be asymptomatic in their early stages, and people may not be aware that they have fatty liver until it progresses to more advanced stages or causes symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and mild jaundice. Severe cases of fatty liver can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and an increased risk of liver cancer.
Diagnosis of fatty liver typically involves blood tests, imaging studies (such as ultrasound or MRI), and sometimes a liver biopsy to determine the extent of liver damage. Treatment for fatty liver depends on the underlying cause:
- For NAFLD: Lifestyle modifications are key, including weight loss, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing underlying conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol. Medications may be considered in some cases.
- For AFLD: The most effective treatment is to stop drinking alcohol. Depending on the severity of liver damage, medical supervision and support may be necessary to quit alcohol safely.
Fatty Liver Treatment in Ayurveda:
Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Liver Care Kit has been formulated to primarily focus on problems related to non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases, alcohol related liver diseases, Hepatitis, Hemochromatosis, etc. and it effectively provides relief. It consists of the best ayurvedic medicine for Fatty Liver. This kit is made using all herbal and natural ingredients and is safe to use.
It consists of:
- Chandraprabha Vati:
It reduces the level of Uric acid, that ultimately helps to provide relief from the pain in the liver and reduces swelling as well.
Ingredients:
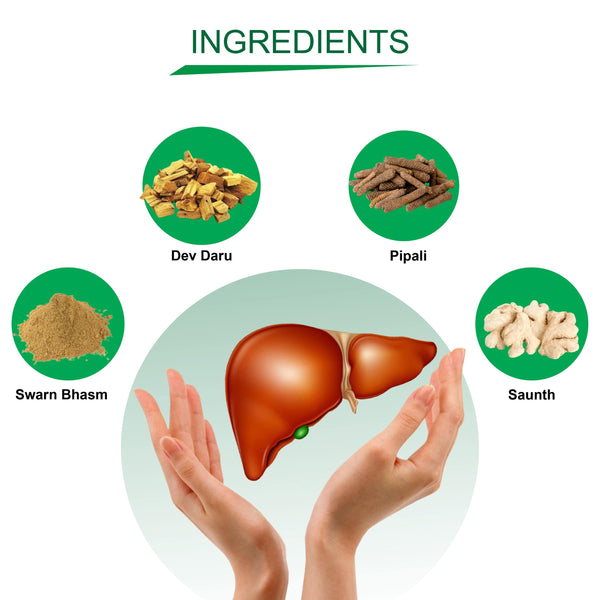
It consists Swarn Bhasm, Vai Vidang, Chitrak Bark, Daruharidra, Devdaru, Camphor, Pipalmool, Nagarmotha, Pippal, Kali MIrch, Yavkshar, Vach, Dhania, Chavya, Gajpipal, Sounth, Sendha Namak, Nishoth, Dantimool,Tejpatra, Chhoti elaichi.
How to use: Consume 1 tablet at night before going to bed.
- Life Guard Advance: Life Guard Advance is a multivitamin syrup; it provides all the necessary vitamins required by our body during pregnancy or anaemia. It helps to boost the immunity power. It is an ideal ayurvedic syrup for fatty liver.
Ingredients: It consists of Arjun Chal, Aswagandha, Gokhru, Satvari, Utangan, Shilajeet, Tulsi, Salimpanja, Amla, Harde, Baheda, Suth,Mari, Pipal.
How to use: Consume Life Guard Advance after light breakfast in the morning.
- Panch Tulsi Drops: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Panch Tulsi Drops has been made with 5 forms of Tulsi that is Ram Tulsi, Van Tulsi, Shyam Tulsi, Vishnu Tulsi and Nimu Tulsi. It helps boost the immune system and build body's resistance. This drop is very effective to fight normal cold, cough, sore throat, etc.
Ingredients: Panch Tulsi Drops consists of extract of 5 types of tulsi namely: Ram Tulsi, Van Tulsi, Shyam Tulsi, Vishnu Tulsi and Nimu Tulsi. It does not include any artificial colors, flavors, etc.
How to use: Add 1-2 drops of Panch Tulsi Drops in a cup of tea/coffee or in a glass of water, twice a day.
- Uti Care Syrup: It is useful in Urine Infection and Urine blockages. It also acts as a detoxifier for your body and cleanses your system.
Ingredients: It consists of mainly Varun Chal, Sharpunkha, Gokharu, Punarnava, Amle, Harde, Baheda, Sariva, Swat Chandan, Ashok Bark, Kanchanar, Gullar Fruit, Pipar Bark, Drumstick Bark, Babbol Bark, Dhatkipuspa.
How to use: Consume1 teaspoon thrice a day with cold water or as directed by the physician.
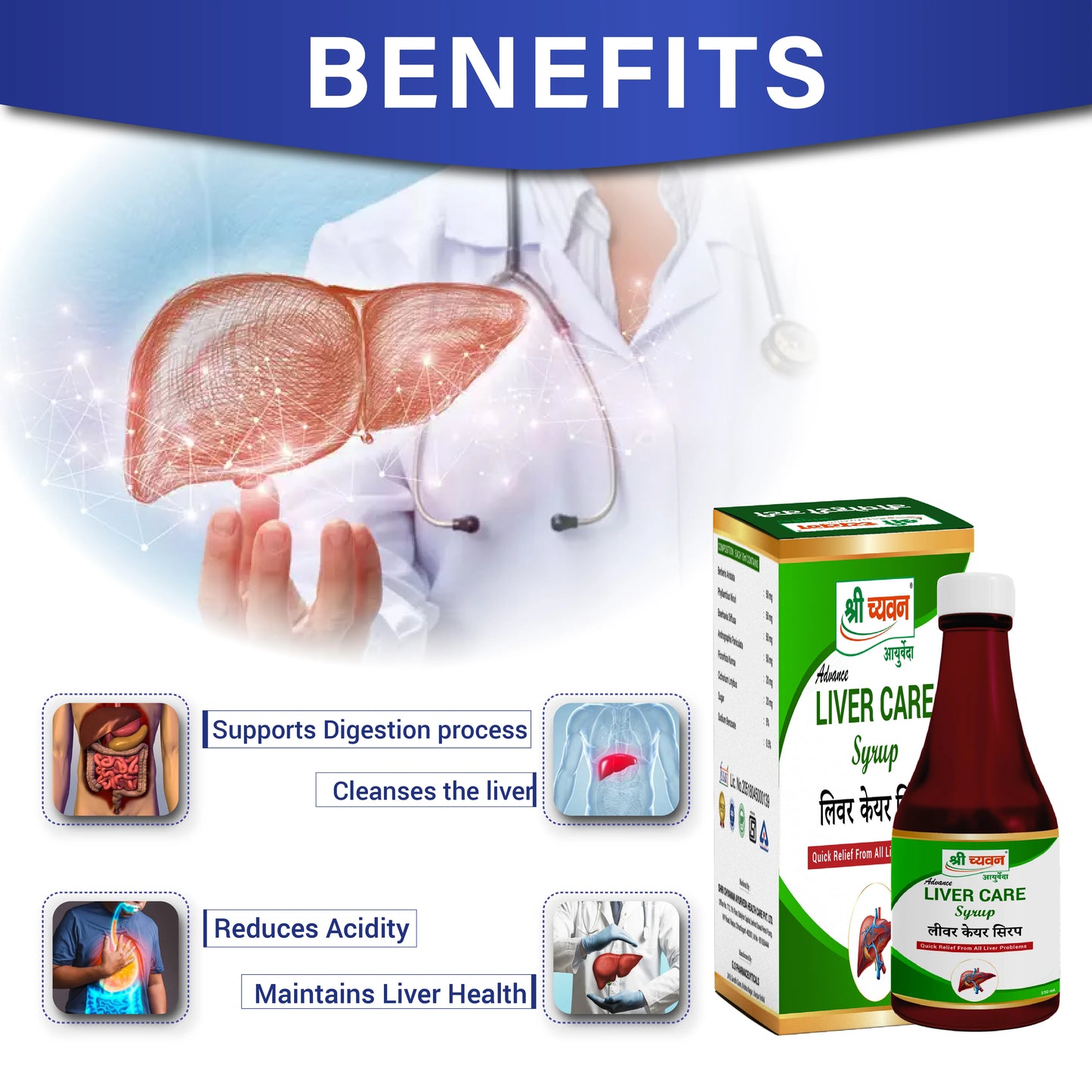
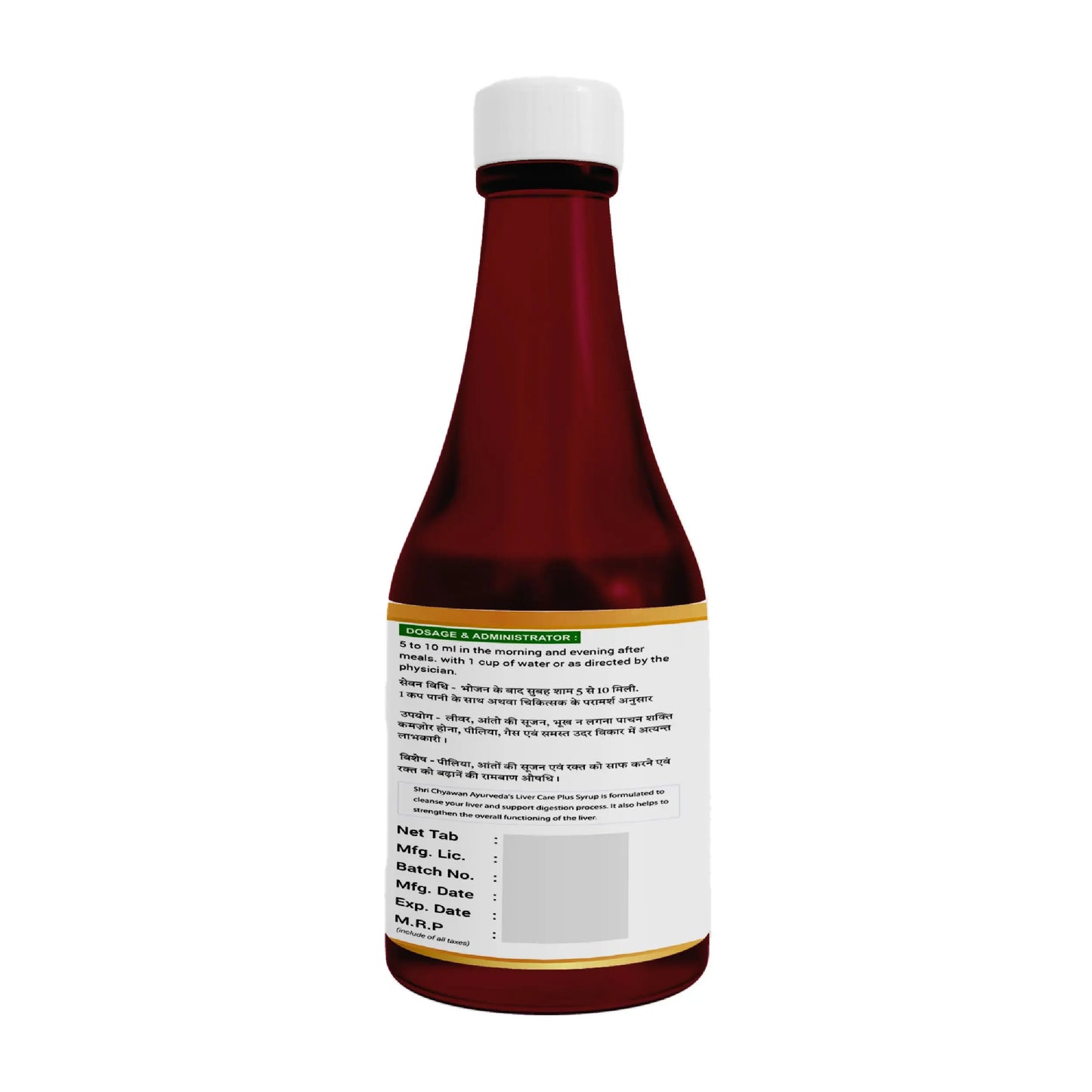
- Liver Care Plus Syrup: It is formulated to cleanse your liver and support digestion process. It also helps to strengthen the overall functioning of the liver.
Ingredients: It consists of Chitrakmul, Amla, Harde, Baheda, Bel Patra, Dhana, Aloe vera, Ajwain, Punarnava, Giloy Satva, Neem Chal, Tulsi.
How to use: Consume 1-2 teaspoonful of Liver Care Syrup, thrice a day or as suggested by your phyician.
Ayurveda, a traditional system of medicine that originated in India, offers holistic approaches to health and wellness, including treatments for various health conditions, including fatty liver. Ayurvedic treatment for fatty liver focuses on restoring balance to the body's doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and improving overall liver health. Ayurveda has the best ayurvedic medicine for fatty liver treatment.
Ayurvedic approaches for management of fatty liver:
- Dietary Modifications: Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet to support liver health. A typical Ayurvedic approach to diet includes:
- Consuming foods that are light and easy to digest.
- Reducing or eliminating processed and fried foods.
- Favoring fresh, organic, and whole foods.
- Incorporating bitter and astringent tastes into the diet, such as leafy greens, bitter gourd, and turmeric, as these are considered beneficial for the liver.
- Herbal Remedies: Ayurvedic herbs may be used to support liver function. Common herbs and preparations include:
- Triphala: A combination of three fruits (amla, bibhitaki, and haritaki) often used to support digestion and detoxification.
- Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa): Known for its potential hepatoprotective properties.
-
Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
-
Detoxification (Panchakarma): Ayurveda utilizes various detoxification procedures to remove toxins from the body. Panchakarma therapies may include oil massages (abhyanga), herbal enemas (basti), and nasal irrigation (nasya) to support liver detoxification.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Ayurveda promotes a balanced lifestyle that includes:
- Stress management through practices like yoga and meditation.
- Maintaining a regular daily routine (dinacharya).
- Ensuring proper sleep and rest.
-
Yoga and Physical Activity: Certain yoga poses and exercises may help improve digestion and overall health. Consult with an Ayurvedic practitioner or yoga instructor for suitable practices.
-
Meditation and Pranayama: Practices like mindfulness meditation and pranayama (breath control) can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being, which can indirectly benefit liver health.
- Consultation with an Ayurvedic Practitioner: It's essential to work with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner who can assess your individual constitution (Prakriti) and imbalances (Vikriti) to create a personalized treatment plan.