Liver cirrhosis is a late stage of scarring (fibrosis) of the liver caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. The liver carries out several necessary functions, including detoxifying harmful substances in your body, cleaning your blood, and making vital nutrients.
Cirrhosis can lead to a number of complications, including liver cancer. In the early stages of cirrhosis, you usually have no symptoms. As cirrhosis progresses, symptoms and complications can develop.
Liver cirrhosis is characterized by the scarring (fibrosis) of liver tissue. This scarring gradually replaces healthy liver cells, impairing the liver's normal functions. It typically occurs as a result of long-term liver damage from various causes, such as chronic alcohol abuse, chronic viral hepatitis, or other liver diseases.
As cirrhosis progresses, the liver becomes increasingly damaged and less able to perform its vital functions, which include detoxifying the body, processing nutrients, and producing essential proteins. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications, including fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fluid accumulation in the abdomen, bleeding problems, confusion, and an increased risk of liver cancer.
Cirrhosis is irreversible, but its progression can be slowed or halted with appropriate medical treatment, lifestyle changes (like avoiding alcohol and maintaining a healthy diet), and addressing the underlying causes of liver damage. In severe cases where the liver is severely damaged and no longer functioning adequately, a liver transplant may be necessary to save a person's life. Regular medical monitoring is crucial for individuals with cirrhosis to manage their condition effectively.
What are the causes of Liver Cirrhosis?
Liver cirrhosis can be caused by various factors, and the most common causes include:
-
Chronic Alcohol Abuse: Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption is a leading cause of cirrhosis. The liver metabolizes alcohol, and chronic alcohol abuse can lead to liver inflammation, fatty liver disease, and ultimately, cirrhosis.
-
Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Chronic infections with hepatitis B, C, or D viruses can cause ongoing liver inflammation and damage over many years, leading to cirrhosis if left untreated.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This condition is associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Over time, fat accumulation in the liver can lead to inflammation and cirrhosis in some cases.
-
Autoimmune Liver Diseases: Conditions like autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) involve the immune system attacking the liver, leading to inflammation and scarring.
-
Hemochromatosis: Hemochromatosis is a genetic disorder that causes excessive iron absorption by the body. Over time, the iron accumulates in the liver and other organs, leading to cirrhosis.
-
Wilson's Disease: This rare genetic disorder causes the accumulation of copper in the liver and other tissues, resulting in liver damage and cirrhosis.
-
Biliary Atresia: This congenital condition involves the improper development or blockage of bile ducts in infants, leading to liver damage and cirrhosis if not treated early.
-
Medications and Toxins: Long-term use of certain medications, exposure to toxic substances, or ingestion of poisonous substances can harm the liver and cause cirrhosis.
-
Cystic Fibrosis: People with cystic fibrosis can develop liver disease, including cirrhosis, due to the build-up of thick, sticky mucus in the liver's bile ducts.
-
Infections: Certain parasitic infections, such as schistosomiasis, can lead to liver inflammation and cirrhosis.
- Cryptogenic Cirrhosis: In some cases, the exact cause of cirrhosis remains unknown, and it's referred to as cryptogenic cirrhosis.
What are the symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis?
The symptoms of liver cirrhosis can vary depending on the stage of the disease and the extent of liver damage. In the early stages, cirrhosis may not cause noticeable symptoms, but as the disease progresses, individuals may experience a range of symptoms.
Some common symptoms of liver cirrhosis include:
-
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and weakness are common early symptoms of cirrhosis.
-
Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes (jaundice) is a classic sign of liver dysfunction and is caused by the build-up of bilirubin, a waste product normally processed by the liver.
-
Abdominal Swelling: Cirrhosis can lead to fluid accumulation in the abdomen, causing abdominal swelling and discomfort. This condition is called ascites.
-
Easy Bruising and Bleeding: Liver cirrhosis can result in a decrease in blood clotting factors and platelets, leading to easy bruising and a greater tendency to bleed.
-
Itchy Skin: Skin itching (pruritus) can occur due to the build-up of toxins in the bloodstream that the liver would normally filter out.
-
Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss: Many individuals with cirrhosis experience a reduced appetite, which can lead to unintended weight loss.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive symptoms like nausea and vomiting may occur as the liver's ability to process nutrients is impaired.
-
Pale Stools and Dark Urine: Stools may become pale or clay-colored, while urine may darken due to the inability of the liver to process bilirubin properly.
-
Spider-Like Blood Vessels: Small, spider-like blood vessels may appear on the skin, particularly on the upper body.
-
Cognitive Changes: Cirrhosis can affect brain function, leading to confusion, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating. This condition is known as hepatic encephalopathy.
-
Swelling in the Legs and Ankles: Edema, or fluid retention, can lead to swelling in the lower extremities.
-
Increased Susceptibility to Infections: A compromised liver can reduce the body's ability to fight off infections.
- Unpleasant Breath Odor: Foul-smelling breath (often described as "sweet," "musty," or "fishy") can be a symptom of advanced liver disease.
It's important to note that the severity and combination of symptoms can vary widely among individuals with cirrhosis. Some people may have only a few noticeable symptoms, while others may experience multiple complications. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing cirrhosis and preventing further liver damage.
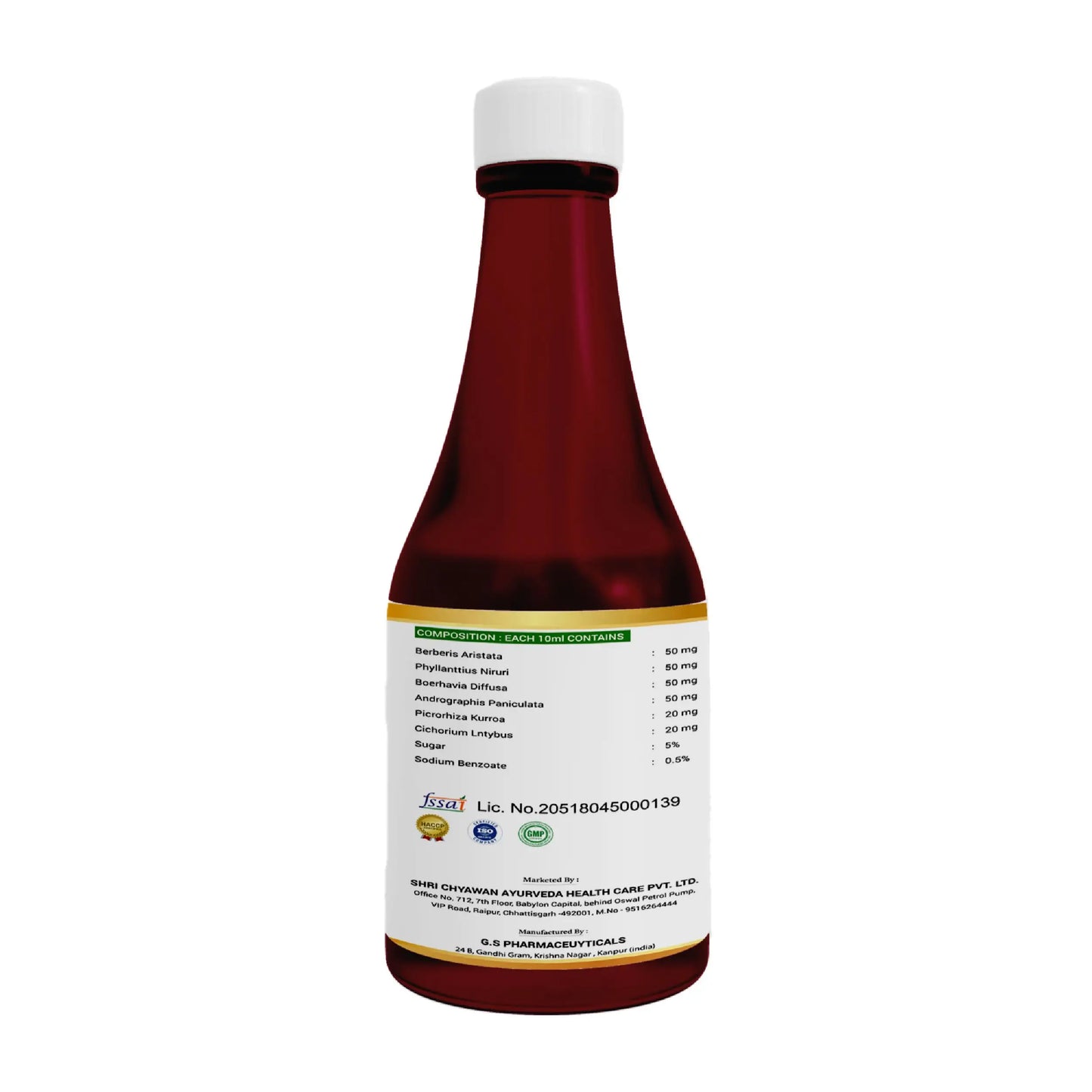
Ayurvedic Treatment for Liver Cirrhosis - Liver Care Syrup:
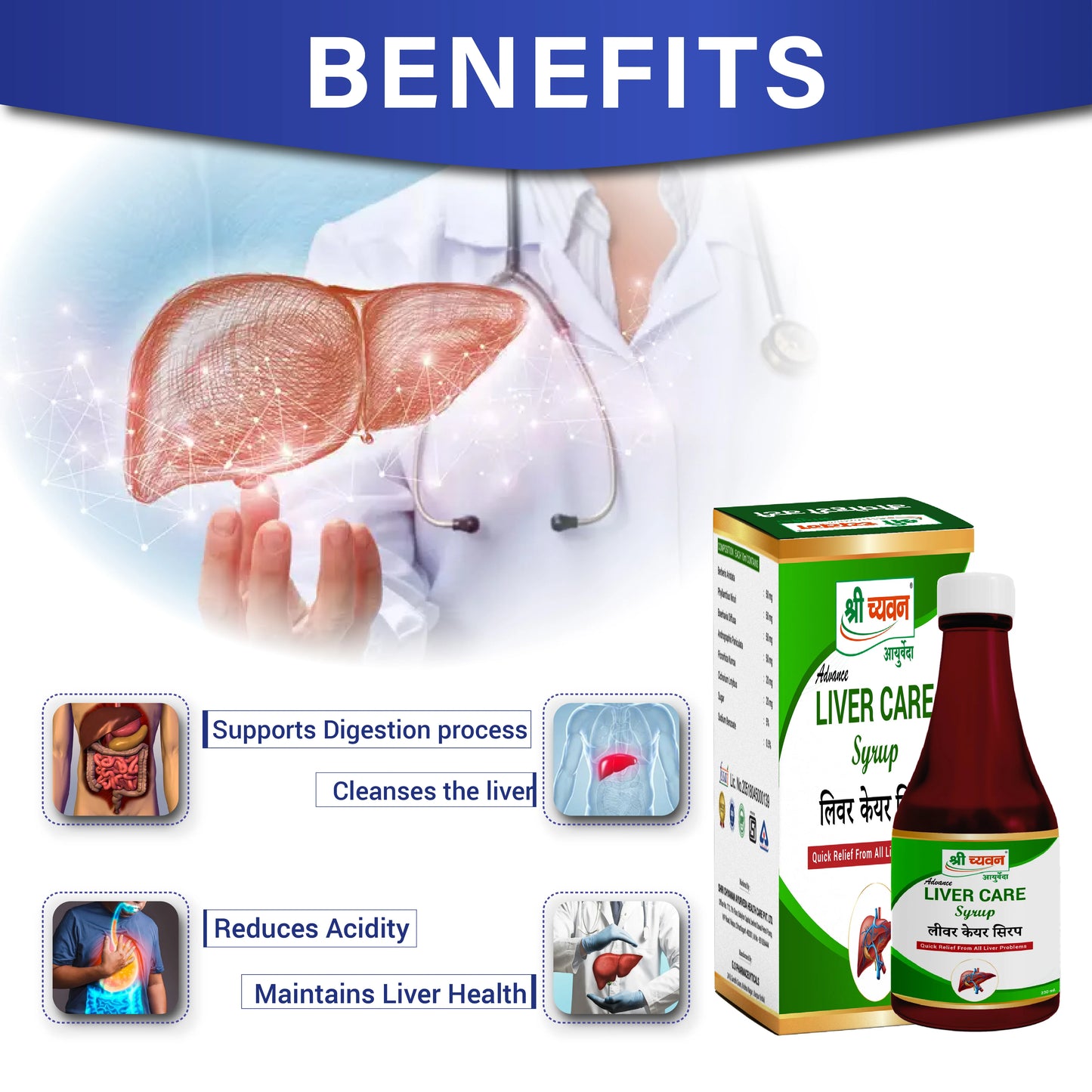
Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's has formulated an ayurvedic liver tonic, Liver Care Syrup with the aim to cleanse your liver and support digestion process. It also helps to strengthen the overall functioning of the liver. It is the best ayurvedic medicine for liver cirrhosis.
Liver Care Syrup Benefits:
-
Reduces Acidity: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Liver Care Syrup, best liver tonic in ayurveda helps in reducing acidity and also reduces acid reflex issues as well.
-
Detoxifier: Liver Care Syrup, an ayurvedic syrup for liver acts as a detoxifying agent and flushes out toxins from your body.
-
Aids in Digestion: It also helps in digestion of food and boosts metabolism and solves constipation problem as well.
- Maintains Liver Health: Regular intake of ayurvedic liver tonic Liver Care Plus Syrup helps to maintain Gut and Liver health.
-
Protection from Liver Damage: Certain ingredients in liver care syrups, such as milk thistle (silymarin) and turmeric (curcumin), are believed to have hepatoprotective properties, meaning they may protect the liver from damage caused by toxins, alcohol, medications, or infections.
-
Liver Regeneration: Some ingredients may support liver cell regeneration and repair, which can be beneficial in cases of liver damage or disease.
-
Balanced Cholesterol Levels: Liver care syrups may help maintain healthy cholesterol levels by supporting the liver's role in cholesterol metabolism.
-
Gut Health: A healthy liver can indirectly benefit gut health by promoting proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Energy and Vitality: When the liver is functioning optimally, it can aid in the metabolism of nutrients and energy production, potentially leading to increased vitality and reduced fatigue.
- Natural Product: It is made from all herbal, ayurvedic ingredients and is natural and safe to use.
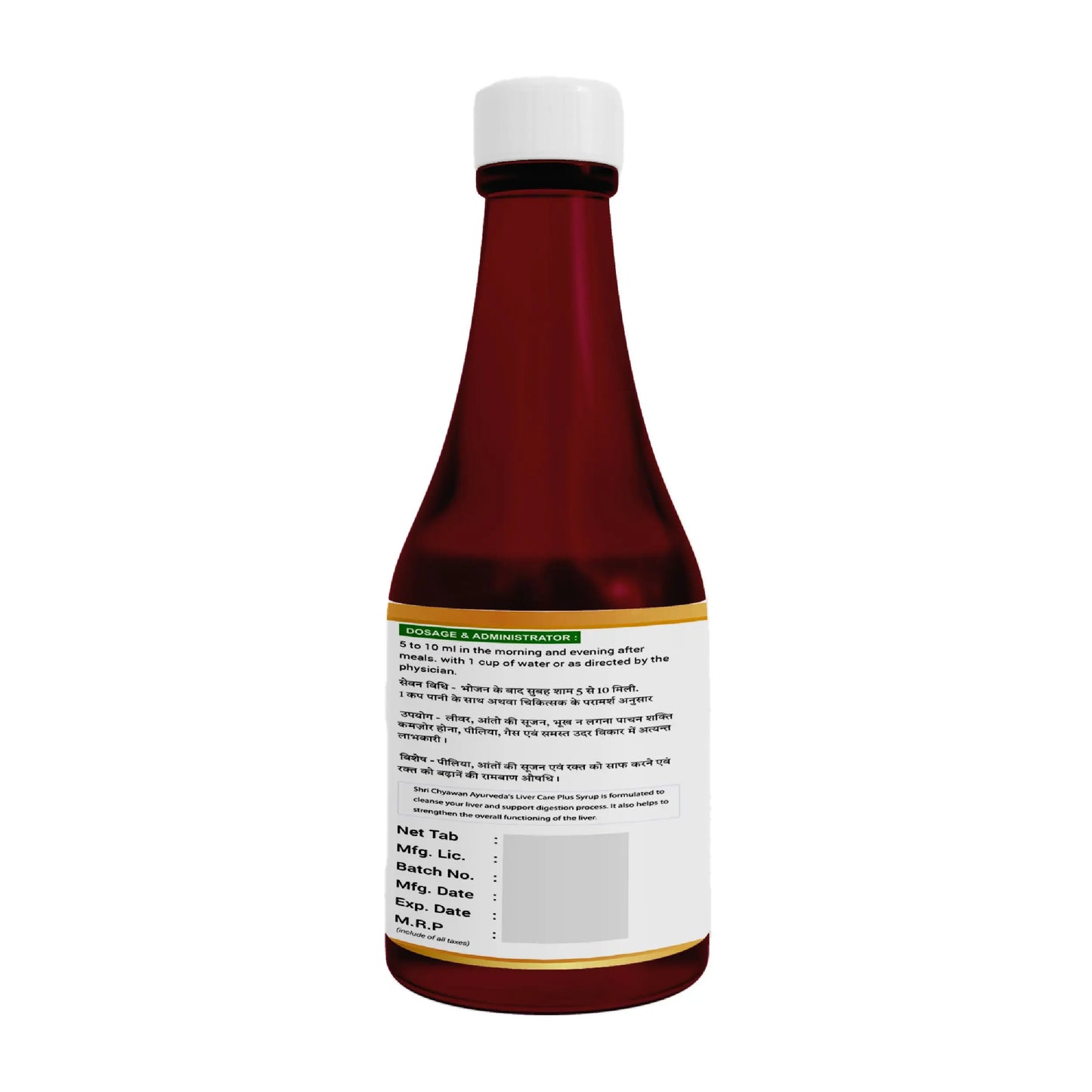
How to use: Consume 1-2 teaspoonful of Liver Care Syrup, thrice a day or as suggested by your physician.
In conclusion, Liver Care Syrup an effective ayurvedic medicine for cirrhosis, offer a range of potential benefits for liver health, including detoxification, liver function support, protection from damage, improved digestion and more. However, it's essential to use these supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional and as part of a comprehensive approach to liver health that includes a healthy lifestyle.