Introduction to Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease involves excess fat accumulation in liver cells, which can lead to inflammation and serious liver conditions. It's categorized into two main types: alcoholic and non-alcoholic.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease occurs when fat makes up over 5-10% of the liver's weight. It can affect anyone, with risk factors including obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
1. Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): Caused by excessive alcohol consumption, leading to fat build-up and potential progression to cirrhosis.
2. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): The most common type, associated with obesity and metabolic issues, ranging from simple fat accumulation to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
3. Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A severe form of NAFLD with inflammation and liver damage, increasing the risk of advanced liver disease.
4. Secondary Fatty Liver Disease: Results from specific medical conditions or medications that contribute to fat accumulation in the liver.
Understanding the Causes
Fatty liver disease develops primarily due to an imbalance between fat accumulation and fat removal in the liver. Key factors include dietary habits, genetic predisposition, and metabolic conditions.
Risk Factors
1. Obesity: Excess body weight significantly increases the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease.
2. Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels are closely linked to fatty liver.
3. High Cholesterol and Triglycerides: Elevated levels of these fats in the blood can lead to liver fat accumulation.
4. Age: The risk increases with age, particularly for those over 50.
Lifestyle Contributors
1. Poor Diet: High consumption of sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats contributes to fat build-up in the liver.
2. Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and metabolic issues, exacerbating liver fat accumulation.
3. Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking can lead to alcoholic fatty liver disease and worsen overall liver health.
4. Medications: Some drugs can contribute to fat accumulation in the liver, including corticosteroids and certain chemotherapy agents.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms
1. Fatigue: A persistent feeling of tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
2. Abdominal Discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen.
3. Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss may occur in some individuals.
4. Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, indicating liver dysfunction.
5. Swelling: Bloating or swelling in the abdomen due to fluid retention.
Diagnostic Tests
1. Blood Tests: Liver function tests (LFTs) can reveal elevated liver enzymes, indicating liver inflammation.
2. Ultrasound: This imaging test can visualize fat deposits in the liver.
3. CT Scan or MRI: More detailed imaging techniques to assess liver fat and damage.
4. Liver Biopsy: A small sample of liver tissue may be taken to determine the severity of liver damage and rule out other conditions.
Fatty Liver Disease Treatments
Lifestyle Changes
1. Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce liver fat.
2. Alcohol Reduction: Limiting or eliminating alcohol consumption helps prevent further liver damage.
Diet Modifications
1. Balanced Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
2. Reduce Sugar and Fat: Limit intake of added sugars and saturated fats to improve liver health.
Exercise Recommendations
1. Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
2. Strength Training: Include resistance exercises to build muscle mass and improve metabolism.
Medical Treatments
1. Regular Check-Ups: Monitor liver function through blood tests and imaging as needed.
2. Tailored Treatment Plans: Work with healthcare providers to create individualized treatment strategies.
Medications
1. Insulin Sensitizers: Drugs like pioglitazone may be prescribed for insulin resistance.
2. Lipid-Lowering Agents: Statins can help lower cholesterol and improve liver function.
Alternative Therapies
1. Supplements: Milk thistle and omega-3 fatty acids may support liver health.
2. Acupuncture: Some studies suggest it might help alleviate symptoms.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
1. Regular Assessments: Schedule follow-ups with healthcare providers to track progress and adjust treatments.
2. Lifestyle Reviews: Periodically evaluate lifestyle and dietary habits for ongoing improvement.
Dietary Approaches for Managing Fatty Liver
Foods to Include
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Lentils, beans, tofu, and low-fat dairy (if applicable).
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Foods to Avoid
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: Limit sodas, candies, and desserts.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Avoid white bread and pastries.
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Cut back on fried and processed foods.
- Excessive Alcohol: Minimize or eliminate alcohol intake.
- Salty Foods: Reduce sodium from processed snacks.
Sample Meal Plan
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with chia seeds and berries.
- Snack: Carrots with hummus.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with black beans and avocado.
- Snack: Mixed nuts.
- Dinner: Tofu stir-fry with vegetables over brown rice.
These approaches can help manage fatty liver while supporting overall health.

Importance of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is crucial for managing fatty liver disease as it helps improve liver function, enhances metabolism, and aids in weight management. It can also reduce inflammation and lower fat accumulation in the liver, promoting overall health and well-being.
Recommended Exercises
1. Aerobic Exercises:- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Jogging
2. Strength Training:
- Bodyweight exercises (push-ups, squats)
- Resistance band workouts
- Light weightlifting
3. Flexibility and Balance:
- Yoga
- Pilates
- Stretching routines
Creating a Workout Routine
1. Frequency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, along with two days of strength training.
2. Duration: Start with 20-30 minutes per session and gradually increase as fitness improves.
3. Variety: Incorporate different types of exercises to keep it interesting and target various muscle groups.
4. Listen to Your Body: Adjust intensity based on your fitness level and health conditions, and consult a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program.
By integrating regular exercise into your routine, you can significantly enhance your efforts to manage fatty liver disease.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Exploring alternative and complementary therapies can provide additional support for managing fatty liver disease. These therapies may complement conventional treatments and enhance overall liver health.
Herbal Remedies
1. Milk Thistle: Known for its active ingredient, silymarin, which may help protect liver cells and promote regeneration.
2. Dandelion Root: Traditionally used to support liver function and detoxification.
3. Artichoke Extract: May improve bile production and support digestion, potentially benefiting liver health.
4. Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may protect the liver.
5. Ginger: Known for its digestive benefits, ginger may also help reduce inflammation in the liver.
Supplements
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in Seeds and Nuts(Chia seeds), these may reduce liver fat levels and improve liver function.
2. Vitamin E: An antioxidant that may help reduce liver inflammation and improve health in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
3. N-acetylcysteine (NAC): An amino acid that may help reduce oxidative stress in the liver.
4. Vitamin D: Adequate levels may be important for overall liver health and function.
5. Probiotics: May support gut health and improve the gut-liver axis, potentially benefiting liver function.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new herbal remedies or supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
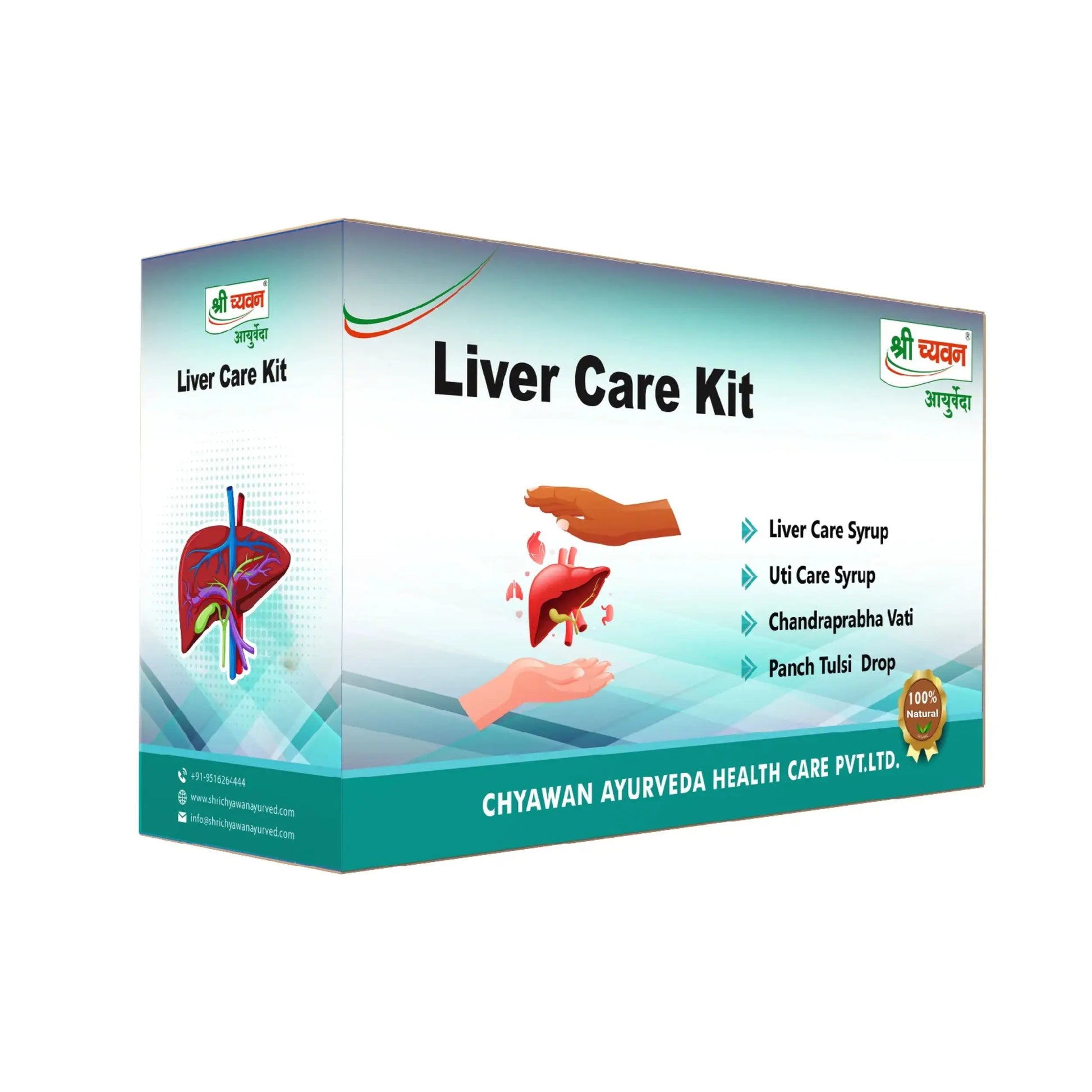
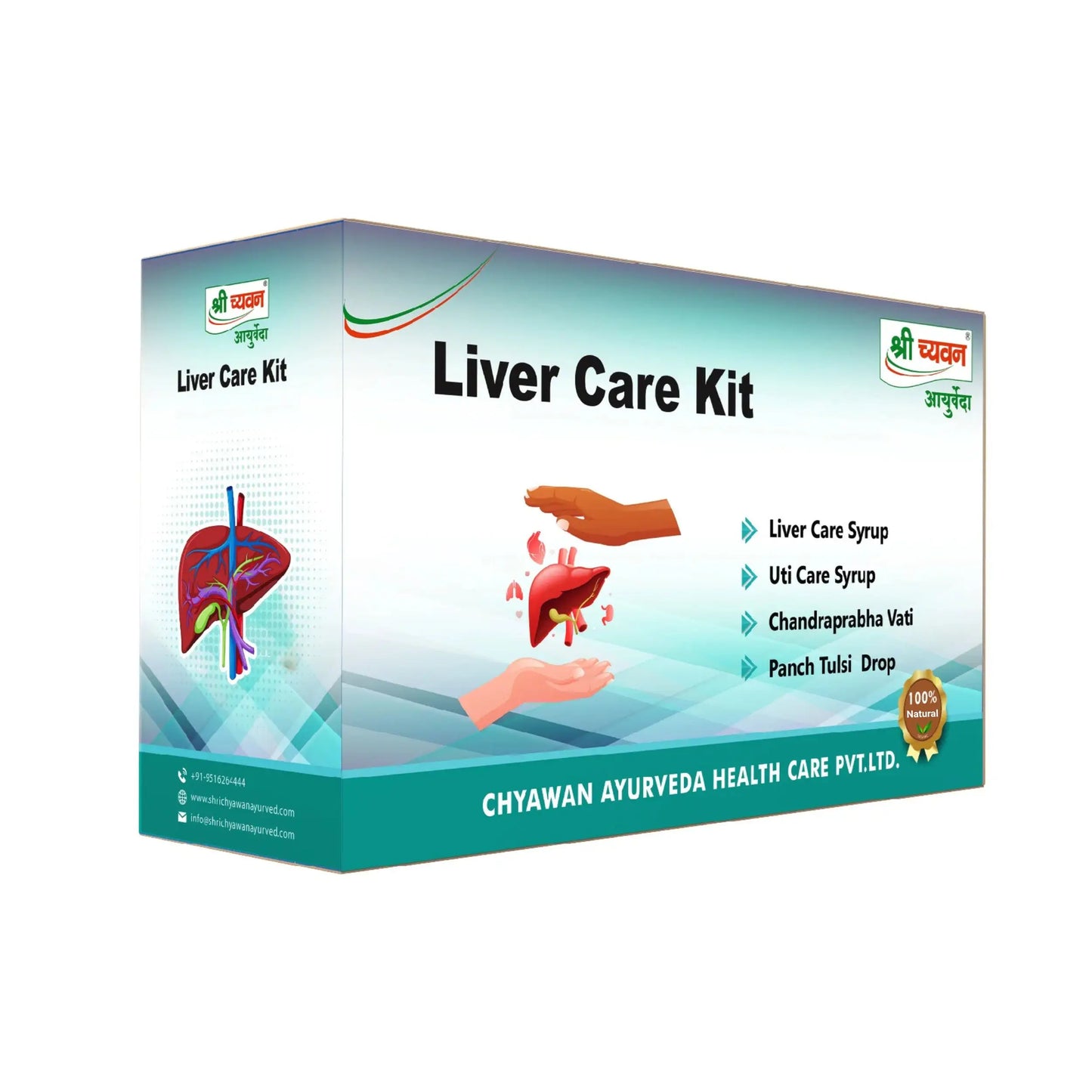
Sri Chyawan Ayurveda's Liver Care Kit
Product Description: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Liver Care Kit has been formulated to primarily focus on problems related to non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases, alcohol-related liver diseases, Hepatitis, Hemochromatosis, etc. and it effectively provides relief. This kit is made using all herbal and natural ingredients and is safe to use. It consists of:
1. Chandraprabha Vati:
It reduces the level of Uric acid, which ultimately helps to provide relief from the pain in the liver and reduces swelling as well.
Ingredients:
It consists Swarn Bhasm, Vai Vidang, Chitrak Bark, Daruharidra, Devdaru, Camphor, Pipalmool, Nagarmotha, Pippal, Kali Mirch, Yavkshar, Vach, Dhania, Chavya, Gajpipal, Sounth, Sendha Namak, Nishoth, Dantimool, Tejpatra, Chhoti elaichi.
How to use: Consume 1 tablet at night before going to bed.
2. Panch Tulsi Drops: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Panch Tulsi Drops have been made with 5 forms of Tulsi that is Ram Tulsi, Van Tulsi, Shyam Tulsi, Vishnu Tulsi and Nimu Tulsi. It helps boost the immune system and build body's resistance. This drop is very effective to fight normal cold, cough, sore throat, etc.
Ingredients: Panch Tulsi Drops consist of extract of 5 types of tulsi namely: Ram Tulsi, Van Tulsi, Shyam Tulsi, Vishnu Tulsi, and Nimu Tulsi. It does not include any artificial colors, flavors, etc.
How to use: Add 1-2 drops of Panch Tulsi Drops in a cup of tea/coffee or in a glass of water, twice a day.
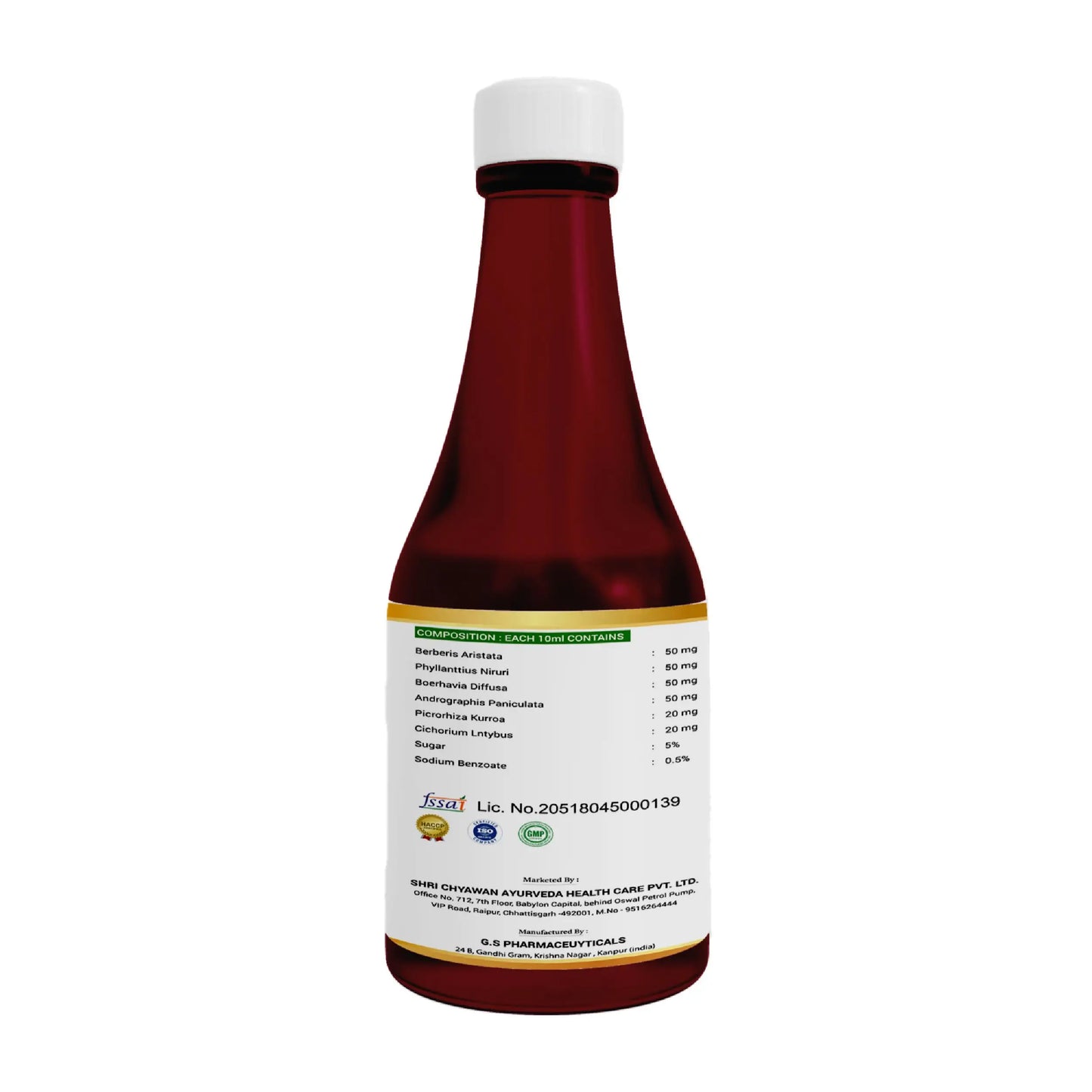
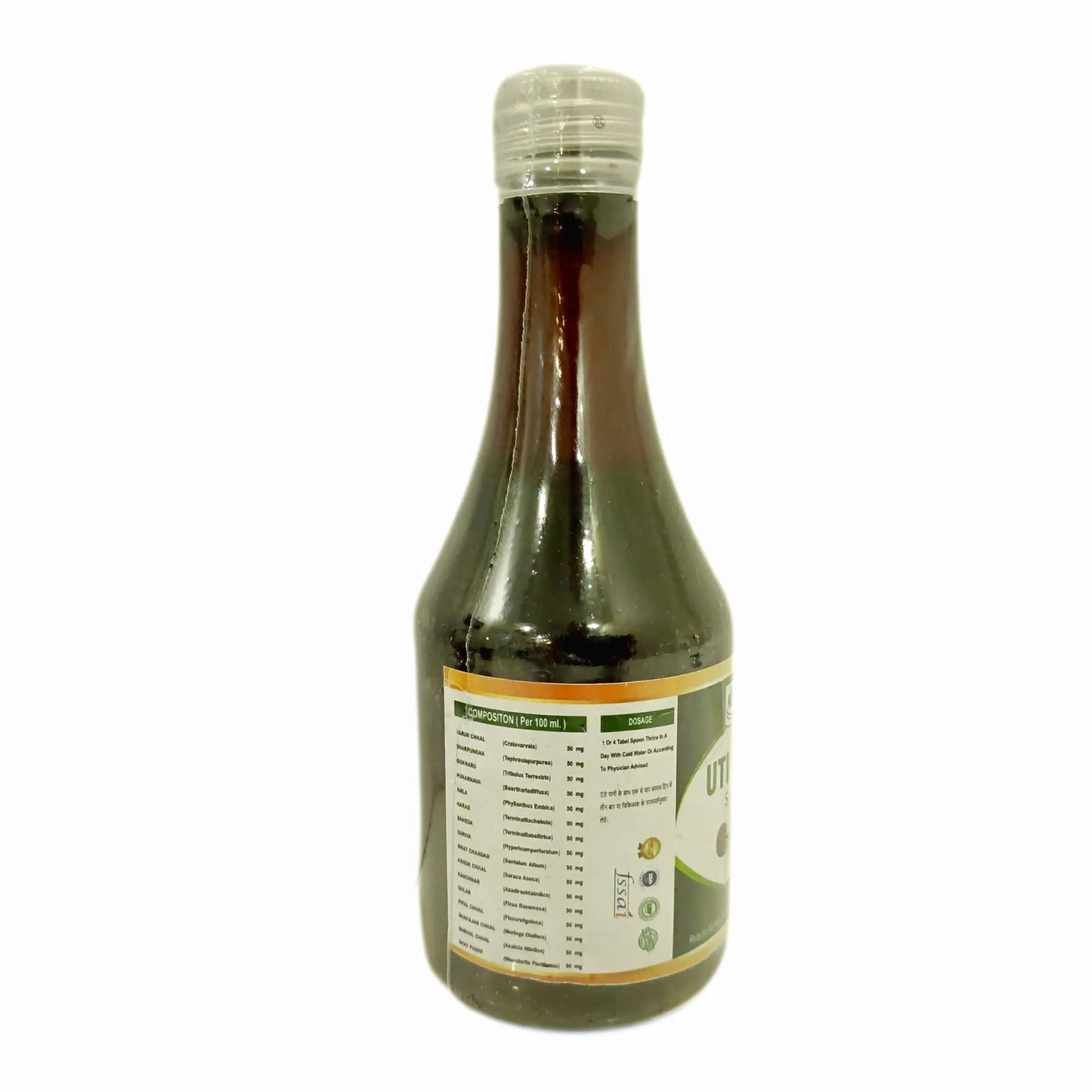
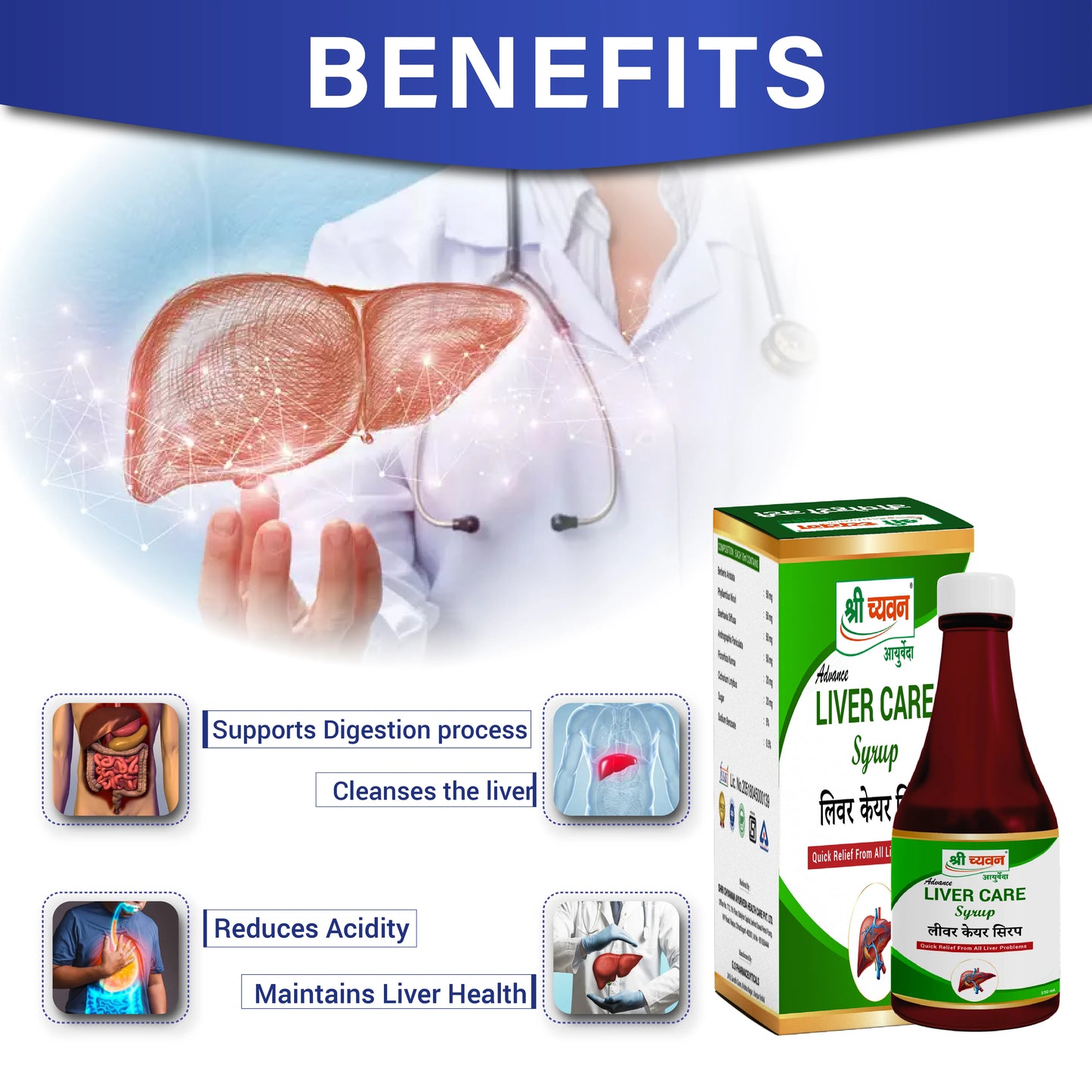
3. Uti Care Syrup: It is useful in Urine Infection and Urine blockages. It also acts as a detoxifier for your body and cleanses your system. It is an effective ayurvedic syrup for fatty liver treatment
Ingredients: It consists of mainly Varun Chal, Sharpunkha, Gokharu, Punarnava, Amle, Harde, Baheda, Sariva, Swat Chandan, Ashok Bark, Kanchanar, Gullar Fruit, Pipar Bark, Drumstick Bark, Babbol Bark, Dhatkipuspa.
How to use: Consume 1 teaspoon thrice a day with cold water or as directed by the physician.
4. Liver Care Syrup: An ayurvedic syrup for fatty liver is formulated to cleanse your liver It also helps to strengthen the overall functioning of the liver.
Ingredients: It consists of Chitrakmul, Amla, Harde, Baheda, Bel Patra, Dhana, Aloe vera, Ajwain, Punarnava, Giloy Satva, Neem Chal, and Tulsi.
How to use: Consume 1-2 teaspoonful of Liver Care Syrup, thrice a day or as suggested by your physician.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Fatty liver disease is a growing concern, characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and the various types is crucial for effective management. Key treatments include lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medical interventions. Emphasizing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and potentially beneficial alternative therapies can significantly enhance liver health and overall well-being.
Encouragement for Seeking Treatment
If you suspect you have fatty liver disease or have been diagnosed, seeking treatment is vital. Early intervention can prevent progression to more severe liver conditions. Collaborate with healthcare professionals to create a personalized management plan that includes lifestyle changes, dietary guidance, and regular monitoring. Taking proactive steps towards managing your liver health is essential for a healthier future. Remember, you're not alone—support is available, and positive changes can lead to significant improvements in your condition.
Free Consultation with our Expert Doctor- 📞📞 95162 64444